Overview of the Java Collections Framework
Introduction
The purpose of this post is to provide an overview of the Collections and help you get that big picture of the Java Collections Framework.
The Java Collections Framework is a set of classes and interfaces that implement commonly reusable collection data structures. It provides interfaces that define various collections as well as classes that implement them.
Collections make our lives easy, because whenever we need to use any data structure or algorithm, we don’t need to write our own implementation. We can directly use it in our program with the help of the Collections Framework.
Collections in Java have several classes and interfaces, but we will not cover each and every one of them now. Instead, let us look at a some of the most commonly used ones.
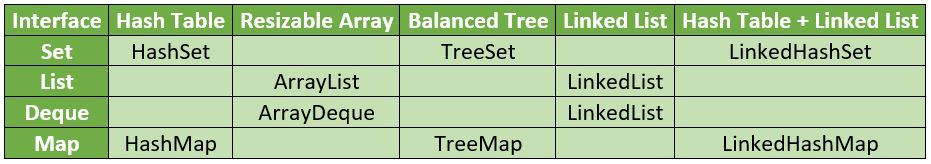
List
List is an ordered collection, also known as a sequence. List may contain duplicate elements. Elements can be inserted or accessed using a zero-based index.
Two mostly used implementations of the List interface are:
- ArrayList
- LinkedList
ArrayList - It is a resizable-array implementation of the List interface.
LinkedList - It is a doubly-linked list implementation of the List and Deque interfaces.
Set
Set is a collection that cannot contain duplicate elements. It may contain at most one null element (not more than one because no duplicates are allowed in a set).
There are three main implementations of the Set interface:
- HashSet
- LinkedHashSet
- TreeSet
HashSet - It stores its elements in a hash table. HashSet has best performance among all the implementations, but it makes no guarantees concerning the order of iteration.
LinkedHashSet - It stores its elements in a hash table with a linked list. Here, the insertion order is preserved.
TreeSet - It stores its elements in a red-black tree, which is a self-balancing binary search tree. It is substantially slower than HashSet, but the elements are ordered based on their value.
Map
Map is an object that maps keys to values. A map cannot contain duplicate keys.
There are three primary implementations of the Map interface:
- HashMap
- LinkedHashMap
- TreeMap
HashMap - It makes no guarantees concerning the order of iteration.
LinkedHashMap - The elements are ordered based on the order they were inserted.
TreeMap - It stores its elements in a red-black tree. It is substantially slower than HashMap, but the elements are ordered based on their value.
Stack
Stack is a linear data structure which follows the Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) approach, where the last element inserted is the first one to be removed.
To make use of stack in our programs, we can either use the Stack class or use an implementation of the Deque interface such as ArrayDeque or LinkedList to implement a stack.
Queue
Queue is a linear data structure which orders elements in a First-In-First-Out (FIFO) manner.
For implementing queue, we can use an implementation of the Deque interface such as ArrayDeque or LinkedList.