HTTPS for WebSockets App on AWS
In this post, we will first see how to enable HTTPS on your WebSockets application. Then we will see how to automatically redirect from HTTP to HTTPS.
I’m hosting my app on AWS Elastic Beanstalk, so in this post I’ll be referring to Elastic Beanstalk whenever needed. But the process should mostly be the same for other AWS products involving load balancers.
If you are using WebSockets in your application, then it is most likely that you have configured your load balancer to listen on TCP. If you are having trouble setting up your WebSockets app, refer my post WebSockets with AWS Elastic Beanstalk.
Enabling HTTPS
To use HTTPS/SSL with Elastic Beanstalk, we need to assign a certificate to the environment’s load balancer. We will terminate SSL connections at our load balancer, and backend connections between the load balancer and EC2 instances will use TCP. This approach takes the least work, and this is what I’m currently using for my application. If you are looking for something else, refer AWS Documentation on configuring HTTPS.
If you haven’t already, get a free SSL certificate for your domain name from AWS Certificate Manager (ACM).
Then open your Amazon EC2 Console, and in the sidebar, click on Load Balancers under Load Balancing section. Then select your load balancer, and in the bottom pane select the Listeners tab.
Now click on on Edit, and add a new listener with the following values:
Load Balancer Protocol: SSL (Secure TCP) and Load Balancer Port: 443
Instance Protocol: TCP and Instance Port: 80
In the SSL Certificate column, choose your SSL certificate from ACM. After you are done, your Listeners tab should look like this:
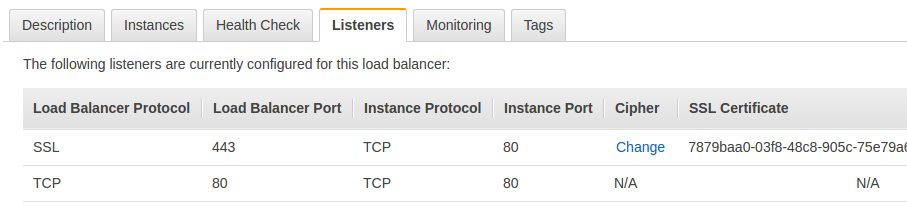
Now, you can verify that HTTPS is working by going to your application’s domain like https://<your domain name>. But we are only partly done. If we visit the domain without https://, we won’t be automatically redirected to HTTPS. Let’s fix that.
Troubleshooting
If the HTTPS connection is failing, open the console and check for errors.
If you are getting Mixed Content Errors, replace all http:// links on your website with https://. For more info, refer MDN Web Docs on fixing a website with blocked mixed content.
Also make sure that you are not connecting to a http:// link in your client side socket connection. Either connect over https:// or leave out the URL like shown below.
var socket = io.connect();When a URL is not specified, as in this case, Socket.io uses the domain and port from the current web page. More info in this StackOverflow answer.
Resolve all the errors and HTTPS should be working.
Redirecting HTTP to HTTPS
Redirecting HTTP to HTTPS can be done by simply checking the X-Forwarded-Proto request header. The X-Forwarded-Proto request header contains the protocol (HTTP or HTTPS) that a client used to connect to the load balancer.
The load balancer stores the protocol in this header and forwards it to our server. In our server, we inspect the X-Forwarded-Proto request header, and if it is HTTP, we redirect to HTTPS.
// redirect HTTP to HTTPS
app.use(function(req, res, next) {
if(req.get('X-Forwarded-Proto') === 'http') {
res.redirect('https://' + req.get('Host') + req.url);
} else {
next();
}
});Add this above code snippet in your server file.
It is important to note that a load balancer only forwards this X-Forwarded-Proto header if a connection is made over HTTP or HTTPS. But since we are using WebSockets, we are listening on TCP. So, this header isn’t forwarded to our server.
So, how do we check if the request is made over HTTP?
One solution is to enable Proxy Protocol, but this requires more configuration.
Another workaround which I found from this StackOverflow answer solves the problem in a much simpler way. So, let’s implement it.
Modify Load Balancer Protocol and Instance Protocol from TCP to HTTP. Now, the Listeners tab should look like this:
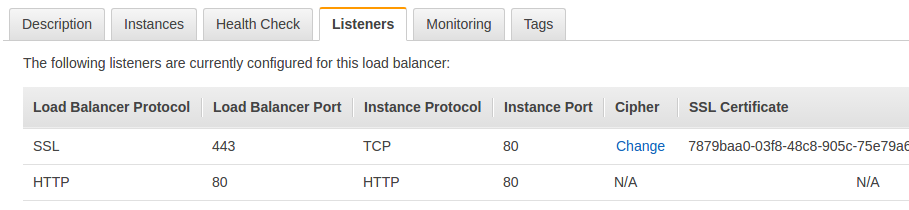
So now if the client connects over HTTP, the load balancer forwards the X-Forwarded-Proto header to our server because the connection is made over HTTP. And using the above code snippet on our server, we are inspecting the header and redirecting to HTTPS/SSL when a user connects on HTTP. Problem solved!